Camera Controls
V4L2 controls and parameters.
Used to adjust basic parameters like:
- image quality
- exposure time, gain, white balance, format, ...
- Region of interest (ROI)
- up to 8x cropping regions (depending on sensor support)
Also used for configuring more complex setups which require for example:
- Synchronization between multiple cameras and/or light sources
- Sequential image capture with different exposure times (HDR)
- Sequential image capture with different light sources
Framerate
Default way of controlling the frame capture interval.
Controlled through the PARM V4L2 interface:
| V4L2 IOCTL | qamlib | Description |
|---|---|---|
VIDIOC_G_PARM | Camera.get_framerate() | Get current framerate |
VIDIOC_S_PARM | Camera.set_framerate() | Set framerate |
VIDIOC_ENUM_FRAMEINTERVALS | Camera.get_framerates() | List possible framerates (for a given image size and format) |
The framerate parameter only has effect when using the self timed trigger mode (which is the default trigger mode).
Other trigger modes can be used when more complex control of the frame capture is desired. In this case the set framerate will be ignored.
V4L2 Controls
Controls are divided in "normal" controls (which only have a single value) and "extended" controls (which can have payload: e.g. arrays or structures).
It is generally easier to always use the extended control interface as it works for both types and allows getting/setting multiple controls simultaneously.
| V4L2 IOCTL | qamlib | Description |
|---|---|---|
VIDIOC_G_CTRL | Camera.get_control() | Get value of a user control |
VIDIOC_S_CTRL | Camera.set_control() | Set value of a user control |
VIDIOC_G_EXT_CTRLS | Camera.get_controls() | Get value of extended control(s) |
VIDIOC_S_EXT_CTRLS | Camera.set_controls() | Set value of extended control(s) |
Exposure Time
The amount of time the sensor is exposed to light, in microseconds.
A higher exposure time will result in a brighter image but can also result in motion blur depending on the object speed. Refer to Adjusting Gain and Exposure for more details.
| Name | Type | Unit | Step |
|---|---|---|---|
Exposure time, absolute | Integer | us | Depends on internal factors (typically around 2 - 10 us) |
The exposure time setting will be ignored in certain trigger modes:
Trigger Mode
The different ways to control frame capture.
Can be used for configuring complex setups which require for example:
- Synchronization between multiple cameras and/or light sources
- Sequential image capture with different exposure times (HDR)
- Sequential image capture with different light sources
| Name | Type | Options |
|---|---|---|
Trigger Mode | Menu control | Self timed (default) External trigger External exposure Trigger sequence External trigger sequence |
Self Timed
- Frame capture interval driven by the configured framerate.
- Exposure time controlled by the exposure time V4L2 control.
- Generates Flash OUT pulses that can be used to synchronize other cameras and/or light sources.
- This is the default way to control frame capture.
- Use this mode for single camera setups.
- Use this mode for the master camera of multi-camera setups that require synchronization.
Refer to Camera/Light Synchronization for more details.
External Trigger
- Frame capture triggered by a falling edge on the Trigger IN signal.
- The configured framerate is ignored in this case.
- Exposure time controlled by the exposure time V4L2 control.
- Use this mode on a slave camera of a multi-camera setup in order to synchronize it's frame capture with the master camera. This allows the slave camera to control it's own exposure time.
Refer to Camera/Light Synchronization for more details.
Even when operating in External Trigger mode the camera cannot capture frames
faster than the maximum framerate of the self timed mode
(which is limited by the read-out time of the sensor).
Trigger signals received at faster intervals than what the camera can handle will be ignored.
External Exposure
- Frame capture triggered by a falling edge on the Trigger IN signal.
- The configured framerate is ignored in this case.
- Exposure time controlled by the Trigger IN signal pulse duration.
- The configured exposure time is ignored in this case.
- Use this mode on a slave camera of a multi-camera setup in order to synchronize it's frame capture with the master camera. The exposure time of the slave camera will also be controlled by the master camera.
Refer to Camera/Light Synchronization for more details.
Even when operating in External Trigger mode the camera cannot capture frames
faster than the maximum framerate of the self timed mode
(which is limited by the read-out time of the sensor).
Trigger signals received at faster intervals than what the camera can handle will be ignored.
Trigger Sequence
- Sequence of up to 16 individual exposures with user defined
exposure time,flash time,frame delay, andtrigger delay. - The configured framerate is ignored in this case.
The resulting frame interval is the sum of all configured
frame delays in the sequence. - The "global" configured exposure time is ignored in this case.
All the individual
exposure times must be specified in the sequence. - The "global" external trigger delay is ignored in this case.
Individual
trigger delays can be specified in the sequence. - In the other trigger modes the flash time duration (on the Flash OUT pin)
is automatically controlled by the exposure, this is not the case here.
This value must be specified using the
flash timeparameter of each sequence in order to control up to two external light sources.
The settings that need to be configured for each frame of the sequence are:
- Exposure time: the exposure time (in us) for the frame.
- Frame delay: the delay (in us) between the start of the current frame and the start of the next frame (which needs to obey some timing constrains).
- Flash time: the flash time (in us) for the frame. The ON (flash) time for the illumination source.
- Trigger delay: the extra delay time (in us) to be added to the exposure and/or flash time.
- Flash time delay: whether to add the trigger delay to the flash time (boolean).
This will cause the flash to begin before the exposure if
flash time delayis disabled and atrigger delayis used.
- Flash time delay: whether to add the trigger delay to the flash time (boolean).
This will cause the flash to begin before the exposure if
All these parameters are configured at once in the V4L2 driver via an array of trigger sequence structs.
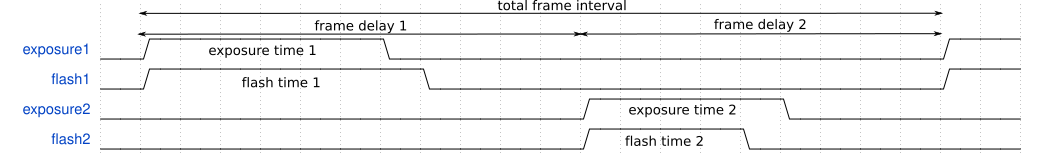 Trigger sequence with 2 exposures and no trigger delay
Trigger sequence with 2 exposures and no trigger delay
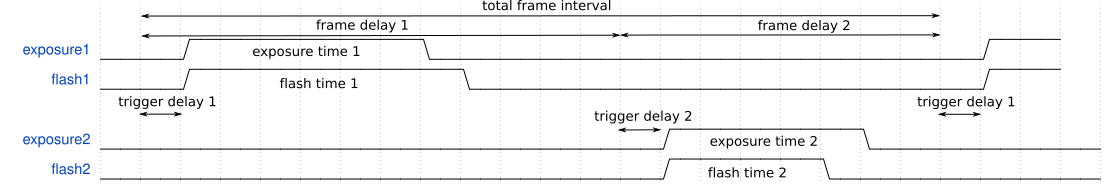 Trigger sequence with 2 exposures, trigger delay and flash time delay
Trigger sequence with 2 exposures, trigger delay and flash time delay
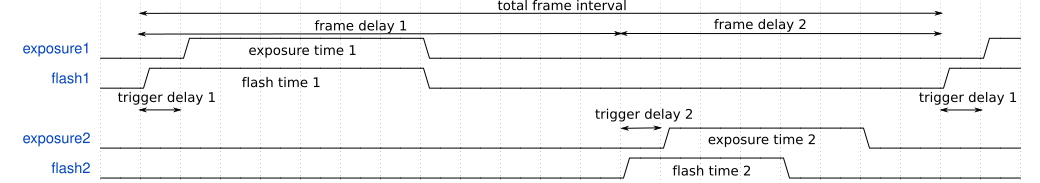 Trigger sequence with 2 exposures, trigger delay and no flash time delay
Trigger sequence with 2 exposures, trigger delay and no flash time delay
The minimal frame delay depends on some internal factors: frame overhead time (FOT) and read-out time (ROT) which are available as read-only V4L2 controls. These timings depend highly on the configured frame "settings" (resolution and bit mode) and therefore need to be re-calculated if any of these parameters change.
The internal timing constraints result in the following formula:
With as the list of exposure times, as the list of frame delays, as the list of flash times, and as the list of trigger delays.
Notice that if flash time delay is disabled then
becomes simply
The requested trigger sequence will be rejected by the driver if the frame delays specified in the trigger sequence fail to comply with this time constraint.
Example
Trigger sequence with 2 frames:
- Image resolution: 1664x17
- desired total framerate: 280 fps
- us
- us
- us
- us
- no trigger delay
Read FOT and ROT from the sensor:
Calculations:
- Minimal :
- Minimal :
- frame interval = 1/280
You can then split the extra delay however you like, e.g. having the second frame as close to the first as possible:
Then qamlib can be used to configure the sequence:
trig_seq.add_exposure(200, 300, 395, 0)
trig_seq.add_exposure(500, 600, 3176, 0)
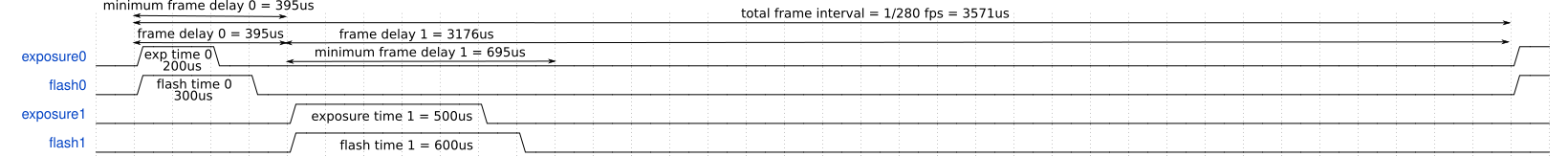 Example trigger sequence with 2 exposures
Example trigger sequence with 2 exposures
Refer to the HDR example from the official qamlib documentation for an example on how to configure a trigger sequence and to the Secondary Flash OUT signal section for details on how to drive a secondary light source.
This trigger mode is a bitstream specific feature, only the following bitstreams have support for it:
- for Sony sensors: draco-tokyo and corna-tokyo
- for CMV/GMAX sensors: draco-copenhagen and lyra-copenhagen
Refer to the bitstreams section for the complete list of supported features per bitstream.
External Trigger Sequence
- Sequential multiple exposures driven by Trigger IN signal (falling edge).
- Analog of external trigger mode for trigger sequences.
- Use this mode on a slave camera of a multi-camera setup in order to synchronize its frame capture with a master camera that uses a trigger sequence. This allows the slave camera to control its own exposure time.
Refer to Camera/Light Synchronization for more details.
Invert Flash Polarity
Inverts the polarity of the Flash OUT signal from active LOW to active HIGH.
Disable Flash
Disables the Flash OUT signal.
Invert Trigger Polarity
Inverts the polarity of the Trigger IN signal from active LOW to active HIGH.
External Trigger delay [us]
Delay frame capture by a specified amount of us after receiving a signal in the Trigger IN pin.
Frame overheadtime
Frame overhead time (FOT). Time between end of sensor exposure and start of sensor read-out.
Read-only control needed in order to calculate the minimum frame delay for trigger sequences. Depends on the configured bit mode (8, 10 or 12 bit) and therefore needs to be re-read if the bit mode is changed.
Read-out time
Frame read-out time (ROT). The time needed to read-out the frame data out of the sensor. Depends on the size of the frame.
Read-only control needed in order to calculate the minimum frame delay for trigger sequences. Depends highly on the configured frame "settings" (resolution and bit mode) and therefore needs to be re-read if any of these parameters change.